*Introduction: Overview of Programming Languages
Programming languages can be categorized into different main groups, each with its unique features and applications. Understanding these categories is essential to comprehend the evolution of programming languages and appreciate their impact on the technological world. Below, the key categories are explained:
1. Machine Code:
Machine code consists of sequences of zeros and ones directly understood by a computer processor. It represents the most fundamental form of programming and is specific to a particular hardware architecture. An example of machine code might look like this: 10110000 01100001.
2. Assembly Languages (Assembly):
Assembly languages are successors to machine code and provide a more human-readable form of programming. These languages translate symbolic instructions into the corresponding machine language. An example of assembly code could look like this:
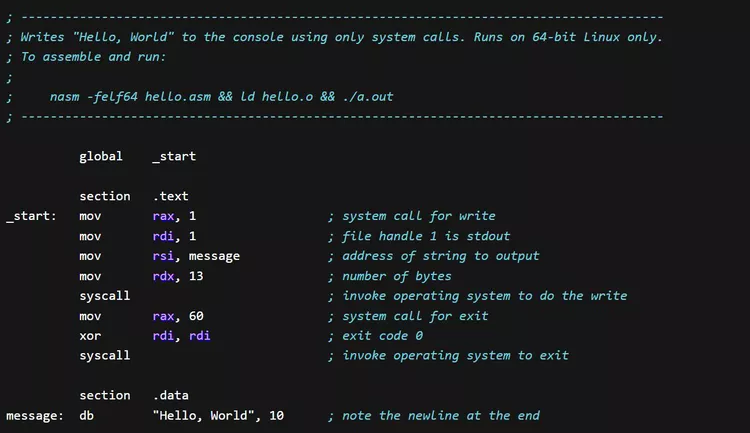
3. High-Level Programming Languages:
High-level programming languages, such as C, Java, and Python, are designed to reduce the complexity of programming. They use readable syntax and provide abstraction from the underlying hardware. Here's an example of a simple program in C:

4. Fourth-Generation Languages (4GL):
Fourth-generation languages are specialized languages designed for specific tasks, like SQL for databases and MATLAB for scientific calculations. They enable users to accomplish complex operations with minimal code. An example SQL query might look like this:
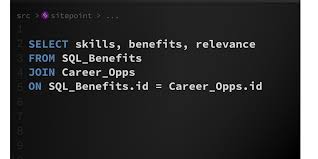
5. Object-Oriented Languages:
Object-oriented languages, such as C++ and Java, organize data into objects containing both data and associated functions. This approach promotes reusability and modularity in the code. Here's an example of a class in Java:
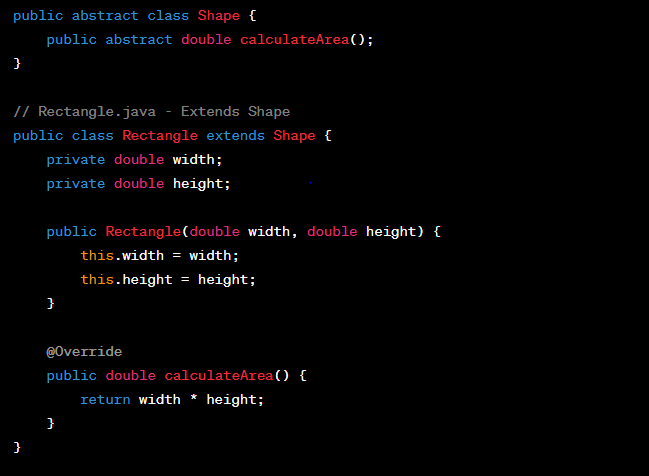
main categories represent the evolution of programming languages, each with its advantages and applications. In the following sections, we will explore some of the most influential programming languages within these categories and discuss their contributions to the world of computer science.












